术前保温和术中保温之间短暂中断与术中低体温发生率有关
术前保温和术中保温之间短暂中断与术中低体温发生率有关
文章图片
文章图片
背景
对于手术时间超过30分钟的手术 , 建议预防不经意的低体温 , 因为低体温会增加心肌缺血、术中失血、输血和伤口并发症的风险 。因此 , 术前保温和术中保温之间的短暂中断可能导致低体温发生 。这项回顾性调查研究的目的是确定术中不经意低体温的发生率是否受保温中断的影响 。
方法
从麻醉记录单中获得术中最低体核温度和保温中断时间 。连续记录患者体核温度 , 如果记录的最低体核温度低于36°C , 则将患者归类为体温过低 。计算低体温发生率与保温中断时间及术中体温过低发生率的相关性 。
结果
本研究共纳入5,084例患者 。术中低体温发生率为15.3% 。麻醉记录单记录19例(0.4%)患者的体温低于35.0°C 。充气加温法中断时间增加与术中低体温发生率增加显著相关(P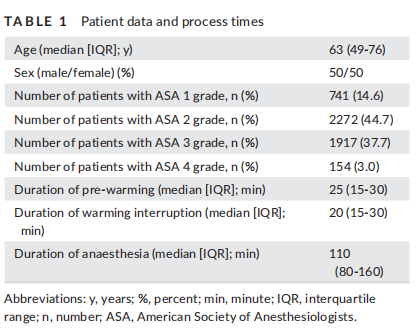
文章图片
文章图片 
文章图片
文章图片 
文章图片
文章图片
结论
术中低体温发生率随着术前保温和术中保温之间充气加温法中断时间的延长而显著增加 。短暂的保温中断可以保留术前保温的效果 , 并与术中低体温发生率相关 。
原始文献来源
Grote R, Wetz A, Br?uer A, Menzel M. Short interruptions between pre-warming and intraoperative warming are associated with low intraoperative hypothermia rates. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2020;64:489–493.
Short interruptions between pre-warming and intraoperativewarming are associated with low intraoperative hypothermia
rates
Abstract
Background:Prevention of inadvertent hypothermia is recommended for procedures >30 minutes because hypothermia increases the risk of myocardial ischemia, intraoperative blood loss, transfusion and wound complications. Therefore, short warming interruptions between pre-warming and intraoperative warming might result in lower hypothermia rates. The aim of this retrospective investigation was to determine whether the incidence of inadvertent intraoperative hypothermia was affected by the warming interruption.
Methods:The lowest intraoperative body core temperature value and the warming interruption time were taken from anaesthesia records. Body core temperature was recorded continuously, and a patient was classified to be hypothermic if the lowest recorded temperature value was Results:Five thousand eighty-four patients were analysed. The intraoperative hypothermia rate was 15.3%. Nineteen patients (0.4%) had a recorded temperature of 20 minutes showed significantly higher hypothermia rates than those with interruptions of ≤20 minutes (P Conclusion:Intraoperative hypothermia rates increased significantly with longer forced-air warming interruptions between pre-warming and intraoperative warming. Short warming interruptions can preserve the effect of pre-warming and are associated with low intraoperative hypothermia rates.
【术前保温和术中保温之间短暂中断与术中低体温发生率有关】来源:健康界
推荐阅读
- 中老年人如何保养心脏?这6个方面做到位,心脏更健康
- 假期吃喝连轴转,警惕牙齿患上“春节病”,打响“牙齿保卫战”
- 冬季老年人养生保健知识——健康饮食
- 叮咚买菜推出“保萝工坊” 意在布局烘焙赛道
- 今天是大寒!大家注意保暖
- 王者荣耀:ttg正式公布接下来的决定,教练可能都保不住了
- 王者荣耀:这些皮肤始终保持热门程度,庄周高山流水皮肤现状如何
- 星鸦会像松鼠一样储存冬粮吗?生长在汪清保护地的东北豹会经常上树活动吗?
- 大寒来了!你知道身上最需要保暖的8个部位、8处“暖气”开关吗?
- 大棚花卉走俏春节










